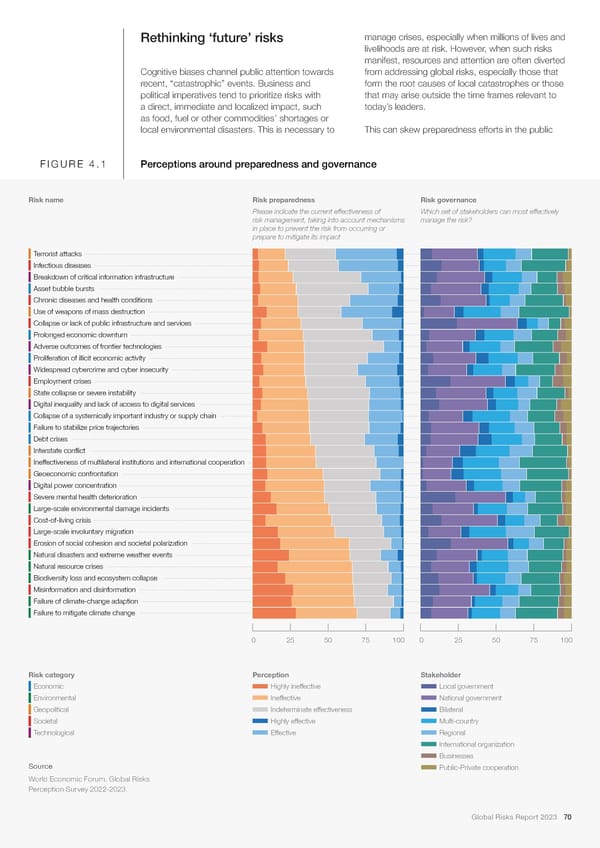
Rethinking ‘future’ risks manage crises, especially when millions of lives and livelihoods are at risk. However, when such risks manifest, resources and attention are often diverted Cognitive biases channel public attention towards from addressing global risks, especially those that recent, “catastrophic” events. Business and form the root causes of local catastrophes or those political imperatives tend to prioritize risks with that may arise outside the time frames relevant to a direct, immediate and localized impact, such today’s leaders. as food, fuel or other commodities’ shortages or local environmental disasters. This is necessary to This can skew preparedness efforts in the public FIGURE 4.1 Perceptions around preparedness and governance Risk name Risk preparedness Risk governance Please indicate the current effectiveness of Which set of stakeholders can most effectively risk management, taking into account mechanisms manage the risk? in place to prevent the risk from occurring or prepare to mitigate its impact Terrorist attacks Infectious diseases Breakdown of critical information infrastructure Asset bubble bursts Chronic diseases and health conditions Use of weapons of mass destruction Collapse or lack of public infrastructure and services Prolonged economic downturn Adverse outcomes of frontier technologies Proliferation of illicit economic activity Widespread cybercrime and cyber insecurity Employment crises State collapse or severe instability Digital inequality and lack of access to digital services Collapse of a systemically important industry or supply chain Failure to stabilize price trajectories Debt crises Interstate conflict Ineffectiveness of multilateral institutions and international cooperation Geoeconomic confrontation Digital power concentration Severe mental health deterioration Large-scale environmental damage incidents Cost-of-living crisis Large-scale involuntary migration Erosion of social cohesion and societal polarization Natural disasters and extreme weather events Natural resource crises Biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse Misinformation and disinformation Failure of climate-change adaption Failure to mitigate climate change 0 25 50 75 100 0 25 50 75 100 Risk category Perception Stakeholder Economic Highly ineffective Local government Environmental Ineffective National government Geopolitical Indeterminate effectiveness Bilateral Societal Highly effective Multi-country Technological Effective Regional International organization Businesses Source Public-Private cooperation World Economic Forum, Global Risks Perception Survey 2022-2023. Global Risks Report 2023 70
 2023 | Global Risks Report Page 69 Page 71
2023 | Global Risks Report Page 69 Page 71