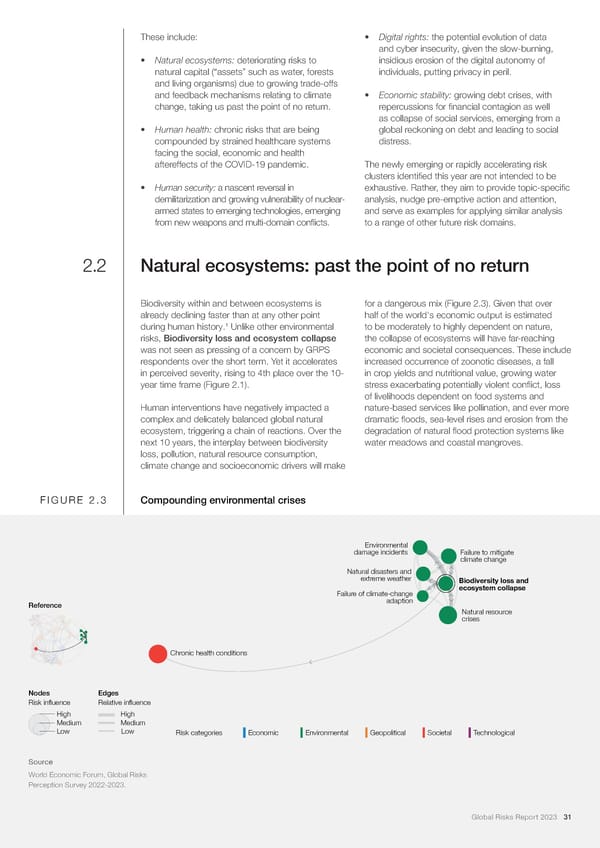
These include: • Digital rights: the potential evolution of data and cyber insecurity, given the slow-burning, • Natural ecosystems: deteriorating risks to insidious erosion of the digital autonomy of natural capital (“assets” such as water, forests individuals, putting privacy in peril. and living organisms) due to growing trade-offs and feedback mechanisms relating to climate • Economic stability: growing debt crises, with change, taking us past the point of no return. repercussions for 昀椀nancial contagion as well as collapse of social services, emerging from a • Human health: chronic risks that are being global reckoning on debt and leading to social compounded by strained healthcare systems distress. facing the social, economic and health aftereffects of the COVID-19 pandemic. The newly emerging or rapidly accelerating risk clusters identi昀椀ed this year are not intended to be • Human security: a nascent reversal in exhaustive. Rather, they aim to provide topic-speci昀椀c demilitarization and growing vulnerability of nuclear- analysis, nudge pre-emptive action and attention, armed states to emerging technologies, emerging and serve as examples for applying similar analysis from new weapons and multi-domain con昀氀icts. to a range of other future risk domains. 2.2 Natural ecosystems: past the point of no return Biodiversity within and between ecosystems is for a dangerous mix (Figure 2.3). Given that over already declining faster than at any other point half of the world's economic output is estimated 1 during human history. Unlike other environmental to be moderately to highly dependent on nature, risks, Biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse the collapse of ecosystems will have far-reaching was not seen as pressing of a concern by GRPS economic and societal consequences. These include respondents over the short term. Yet it accelerates increased occurrence of zoonotic diseases, a fall in perceived severity, rising to 4th place over the 10- in crop yields and nutritional value, growing water year time frame (Figure 2.1). stress exacerbating potentially violent con昀氀ict, loss of livelihoods dependent on food systems and Human interventions have negatively impacted a nature-based services like pollination, and ever more complex and delicately balanced global natural dramatic 昀氀oods, sea-level rises and erosion from the ecosystem, triggering a chain of reactions. Over the degradation of natural 昀氀ood protection systems like next 10 years, the interplay between biodiversity water meadows and coastal mangroves. loss, pollution, natural resource consumption, climate change and socioeconomic drivers will make FIGURE 2.3 Compounding environmental crises Environmental damage incidents Failure to mitigate climate change Natural disasters and extreme weather Biodiversity loss and Failure of climate-change ecosystem collapse Reference adaption Natural resource crises Chronic health conditions Nodes EdgesEdges Risk influence Relative influence High High Medium Medium Low Low Risk categories Economic Environmental Geopolitical Societal Technological Source World Economic Forum, Global Risks Perception Survey 2022-2023. Global Risks Report 2023 31
 2023 | Global Risks Report Page 30 Page 32
2023 | Global Risks Report Page 30 Page 32