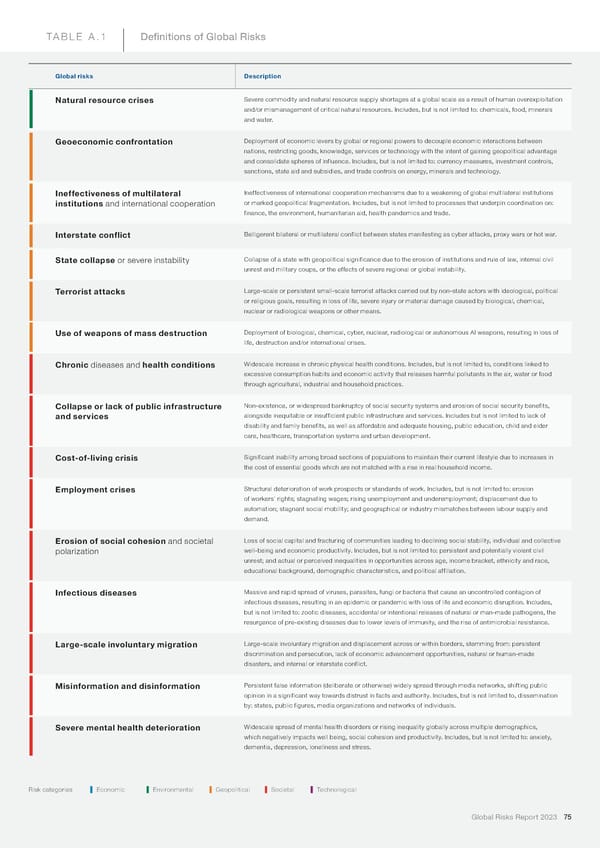
TABLE A.1 De昀椀nitions of Global Risks Global risks Description Natural resource crises Severe commodity and natural resource supply shortages at a global scale as a result of human overexploitation and/or mismanagement of critical natural resources. Includes, but is not limited to: chemicals, food, minerals and water. Geoeconomic confrontation Deployment of economic levers by global or regional powers to decouple economic interactions between nations, restricting goods, knowledge, services or technology with the intent of gaining geopolitical advantage and consolidate spheres of influence. Includes, but is not limited to: currency measures, investment controls, sanctions, state aid and subsidies, and trade controls on energy, minerals and technology. Ineffectiveness of multilateral Ineffectiveness of international cooperation mechanisms due to a weakening of global multilateral institutions institutions and international cooperation or marked geopolitical fragmentation. Includes, but is not limited to processes that underpin coordination on: finance, the environment, humanitarian aid, health pandemics and trade. Interstate conflict Belligerent bilateral or multilateral conflict between states manifesting as cyber attacks, proxy wars or hot war. State collapse or severe instability Collapse of a state with geopolitical significance due to the erosion of institutions and rule of law, internal civil unrest and military coups, or the effects of severe regional or global instability. Terrorist attacks Large-scale or persistent small-scale terrorist attacks carried out by non-state actors with ideological, political or religious goals, resulting in loss of life, severe injury or material damage caused by biological, chemical, nuclear or radiological weapons or other means. Use of weapons of mass destruction Deployment of biological, chemical, cyber, nuclear, radiological or autonomous AI weapons, resulting in loss of life, destruction and/or international crises. Chronic diseases and health conditions Widescale increase in chronic physical health conditions. Includes, but is not limited to, conditions linked to excessive consumption habits and economic activity that releases harmful pollutants in the air, water or food through agricultural, industrial and household practices. Collapse or lack of public infrastructure Non-existence, or widespread bankruptcy of social security systems and erosion of social security benefits, and services alongside inequitable or insufficient public infrastructure and services. Includes but is not limited to lack of disability and family benefits, as well as affordable and adequate housing, public education, child and elder care, healthcare, transportation systems and urban development. Cost-of-living crisis Significant inability among broad sections of populations to maintain their current lifestyle due to increases in the cost of essential goods which are not matched with a rise in real household income. Employment crises Structural deterioration of work prospects or standards of work. Includes, but is not limited to: erosion of workers' rights; stagnating wages; rising unemployment and underemployment; displacement due to automation; stagnant social mobility; and geographical or industry mismatches between labour supply and demand. Erosion of social cohesion and societal Loss of social capital and fracturing of communities leading to declining social stability, individual and collective polarization well-being and economic productivity. Includes, but is not limited to: persistent and potentially violent civil unrest; and actual or perceived inequalities in opportunities across age, income bracket, ethnicity and race, educational background, demographic characteristics, and political affiliation. Infectious diseases Massive and rapid spread of viruses, parasites, fungi or bacteria that cause an uncontrolled contagion of infectious diseases, resulting in an epidemic or pandemic with loss of life and economic disruption. Includes, but is not limited to: zootic diseases, accidental or intentional releases of natural or man-made pathogens, the resurgence of pre-existing diseases due to lower levels of immunity, and the rise of antimicrobial resistance. Large-scale involuntary migration Large-scale involuntary migration and displacement across or within borders, stemming from: persistent discrimination and persecution, lack of economic advancement opportunities, natural or human-made disasters, and internal or interstate conflict. Misinformation and disinformation Persistent false information (deliberate or otherwise) widely spread through media networks, shifting public opinion in a significant way towards distrust in facts and authority. Includes, but is not limited to, dissemination by: states, public figures, media organizations and networks of individuals. Severe mental health deterioration Widescale spread of mental health disorders or rising inequality globally across multiple demographics, which negatively impacts well being, social cohesion and productivity. Includes, but is not limited to: anxiety, dementia, depression, loneliness and stress. Risk categories Economic Environmental Geopolitical Societal Technological Global Risks Report 2023 75
 2023 | Global Risks Report Page 74 Page 76
2023 | Global Risks Report Page 74 Page 76