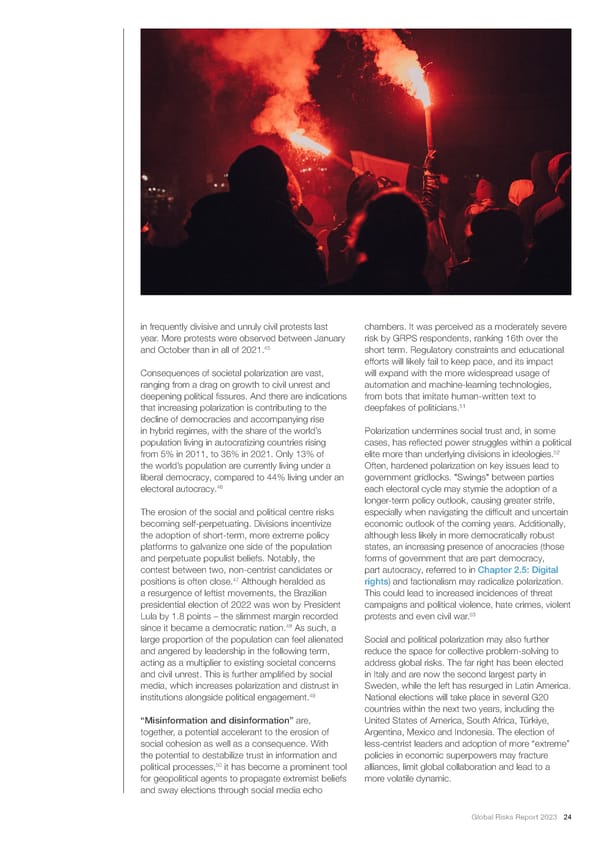
in frequently divisive and unruly civil protests last chambers. It was perceived as a moderately severe year. More protests were observed between January risk by GRPS respondents, ranking 16th over the 45 and October than in all of 2021. short term. Regulatory constraints and educational efforts will likely fail to keep pace, and its impact Consequences of societal polarization are vast, will expand with the more widespread usage of ranging from a drag on growth to civil unrest and automation and machine-learning technologies, deepening political 昀椀ssures. And there are indications from bots that imitate human-written text to that increasing polarization is contributing to the deepfakes of politicians.51 decline of democracies and accompanying rise in hybrid regimes, with the share of the world’s Polarization undermines social trust and, in some population living in autocratizing countries rising cases, has re昀氀ected power struggles within a political 52 from 5% in 2011, to 36% in 2021. Only 13% of elite more than underlying divisions in ideologies. the world’s population are currently living under a Often, hardened polarization on key issues lead to liberal democracy, compared to 44% living under an government gridlocks. "Swings" between parties 46 electoral autocracy. each electoral cycle may stymie the adoption of a longer-term policy outlook, causing greater strife, The erosion of the social and political centre risks especially when navigating the dif昀椀cult and uncertain becoming self-perpetuating. Divisions incentivize economic outlook of the coming years. Additionally, the adoption of short-term, more extreme policy although less likely in more democratically robust platforms to galvanize one side of the population states, an increasing presence of anocracies (those and perpetuate populist beliefs. Notably, the forms of government that are part democracy, contest between two, non-centrist candidates or part autocracy, referred to in Chapter 2.5: Digital 47 positions is often close. Although heralded as rights) and factionalism may radicalize polarization. a resurgence of leftist movements, the Brazilian This could lead to increased incidences of threat presidential election of 2022 was won by President campaigns and political violence, hate crimes, violent Lula by 1.8 points – the slimmest margin recorded protests and even civil war.53 48 since it became a democratic nation. As such, a large proportion of the population can feel alienated Social and political polarization may also further and angered by leadership in the following term, reduce the space for collective problem-solving to acting as a multiplier to existing societal concerns address global risks. The far right has been elected and civil unrest. This is further ampli昀椀ed by social in Italy and are now the second largest party in media, which increases polarization and distrust in Sweden, while the left has resurged in Latin America. 49 institutions alongside political engagement. National elections will take place in several G20 countries within the next two years, including the “Misinformation and disinformation” are, United States of America, South Africa, Türkiye, together, a potential accelerant to the erosion of Argentina, Mexico and Indonesia. The election of social cohesion as well as a consequence. With less-centrist leaders and adoption of more “extreme” the potential to destabilize trust in information and policies in economic superpowers may fracture 50 political processes, it has become a prominent tool alliances, limit global collaboration and lead to a for geopolitical agents to propagate extremist beliefs more volatile dynamic. and sway elections through social media echo Global Risks Report 2023 24
 2023 | Global Risks Report Page 23 Page 25
2023 | Global Risks Report Page 23 Page 25