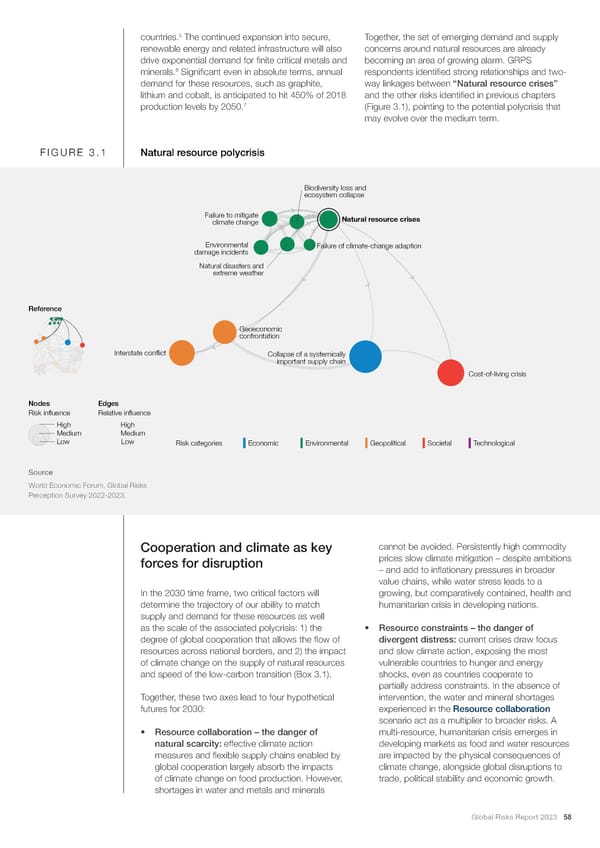
5 countries. The continued expansion into secure, Together, the set of emerging demand and supply renewable energy and related infrastructure will also concerns around natural resources are already drive exponential demand for 昀椀nite critical metals and becoming an area of growing alarm. GRPS 6 minerals. Signi昀椀cant even in absolute terms, annual respondents identi昀椀ed strong relationships and two- demand for these resources, such as graphite, way linkages between “Natural resource crises” lithium and cobalt, is anticipated to hit 450% of 2018 and the other risks identi昀椀ed in previous chapters 7 production levels by 2050. (Figure 3.1), pointing to the potential polycrisis that may evolve over the medium term. FIGURE 3.1 Natural resource polycrisis Biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse Failure to mitigate Natural resource crises climate change Environmental Failure of climate-change adaption damage incidents Natural disasters and extreme weather Reference Geoeconomic confrontation Interstate conflict Collapse of a systemically important supply chain Cost-of-living crisis Nodes EdgesEdges Risk influence Relative influence High High Medium Medium Low Low Risk categories Economic Environmental Geopolitical Societal Technological Source World Economic Forum, Global Risks Perception Survey 2022-2023. cannot be avoided. Persistently high commodity Cooperation and climate as key forces for disruption prices slow climate mitigation – despite ambitions – and add to in昀氀ationary pressures in broader value chains, while water stress leads to a In the 2030 time frame, two critical factors will growing, but comparatively contained, health and determine the trajectory of our ability to match humanitarian crisis in developing nations. supply and demand for these resources as well as the scale of the associated polycrisis: 1) the • Resource constraints – the danger of degree of global cooperation that allows the 昀氀ow of divergent distress: current crises draw focus resources across national borders, and 2) the impact and slow climate action, exposing the most of climate change on the supply of natural resources vulnerable countries to hunger and energy and speed of the low-carbon transition (Box 3.1). shocks, even as countries cooperate to partially address constraints. In the absence of Together, these two axes lead to four hypothetical intervention, the water and mineral shortages futures for 2030: experienced in the Resource collaboration scenario act as a multiplier to broader risks. A • Resource collaboration – the danger of multi-resource, humanitarian crisis emerges in natural scarcity: effective climate action developing markets as food and water resources measures and 昀氀exible supply chains enabled by are impacted by the physical consequences of global cooperation largely absorb the impacts climate change, alongside global disruptions to of climate change on food production. However, trade, political stability and economic growth. shortages in water and metals and minerals Global Risks Report 2023 58
 2023 | Global Risks Report Page 57 Page 59
2023 | Global Risks Report Page 57 Page 59